PKI [ Public key infrastructure ]
PKI: Public key infrastructure is something that establishes and manages public key encryption and digital signature services. For public key encryption to work, digital keys and certificates need to be created, stored, distributed, managed, revoked, used and so on. PKI allows for encryption to do all of these things with software, hardware, protocols, policies, processes and services.
PKI enables what we call public key encryption (aka asymmetric encryption) to be able to use two keys. One key encrypts while the other decrypts. The two keys used are the public key and the private key. The keys are aptly named as one key is available to the public and the other one is private.
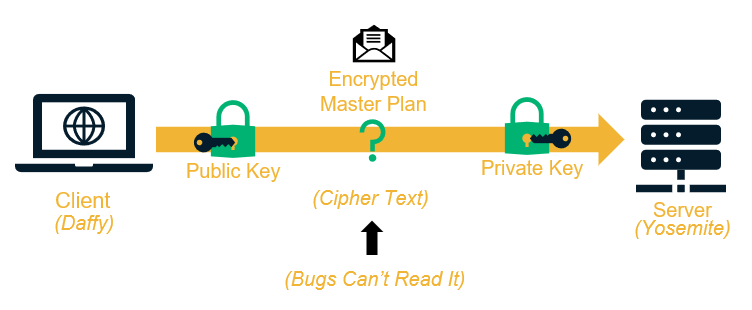
Who Are the Key Players Involved in PKI?
There are three main elements to PKI:
- The key pair, which we just covered is one of them.
- Certificate authorities (CAs) are another. CAs are trusted third-party bodies that develop and manage digital certificates. Trusted is the key word there as CAs hold the prestigious honor of being trusted to issue certificates by meeting ultra-strict criteria established by the CA/Browser Forum (CA/B Forum), an independent group largely made up of representatives from the world’s largest browsers.
- Digital certificates, which are created by the CAs, are the final element. A digital certificate acts as the passports of PKI. Just as you need a passport to travel internationally, you need a digital certificate to travel through PKI. That’s because a PKI digital certificate carries documentation that details information about the key and its owner. It also comes with a signature from the CA, similar to a passport coming with a signoff from the traveler’s government.
These three elements (or “players,” as the title says) make up the inner workings of this infrastructure.
Five Ways That PKI Helps Us in Our Everyday Lives
Web Security
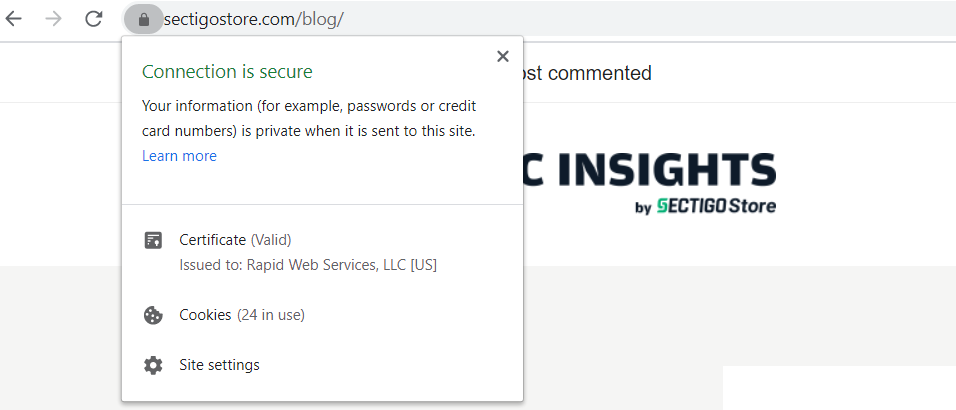
PKI allows for HTTPS to happen. The secure HTTPS protocol allows for browsers and web servers (aka websites) to safely and securely communicate. To have an HTTPS website, you need an SSL/TLS certificate.
By installing an SSL certificate on your website, you receive the aforementioned public and private key pair. The private key is securely housed in the web server, so that a user’s browser can identity a website (server) as legitimate. This allows for users to safely shop, submit personal information, and pay while browsing websites.
Email Security
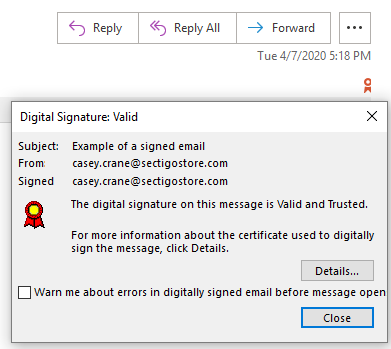
Email is another key area that PKI touches. PKI provides the framework for emails to safely travel from one person to another. This process is known as secure/multipurpose internet mail extension (S/MIME). S/MIME certificates are used to encrypt the email message and digitally sign it, so that the sender and their message can be authenticated. This also helps to prevent bad guys from tampering with emails.
Secure Messaging
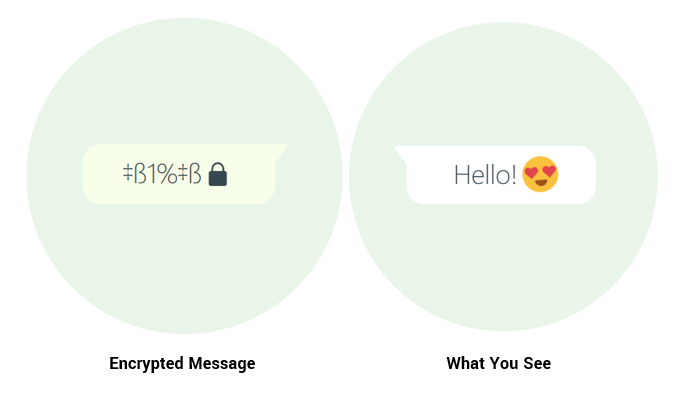
Imagine getting on WhatsApp and feeling like you can’t send a message to your friends without someone intercepting and reading it. It’s a scary thought. PKI makes it more secure to use messaging services like WhatsApp with the use of encryption.
Code/App Signing
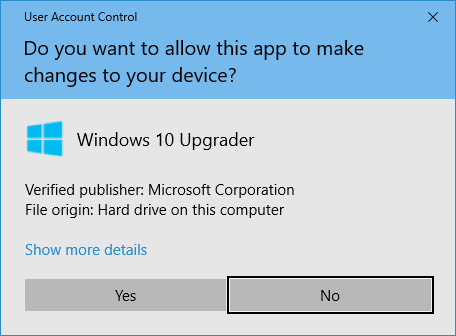
Software developers and publishers using code signing certificates.
These certificates ensure the developer/publisher of the file is who they say they are. PKI enables the code signing certificates to authenticate who the publisher is using public key encryption. It also helps to prevent tampering once the software or application is signed.
Document Signing
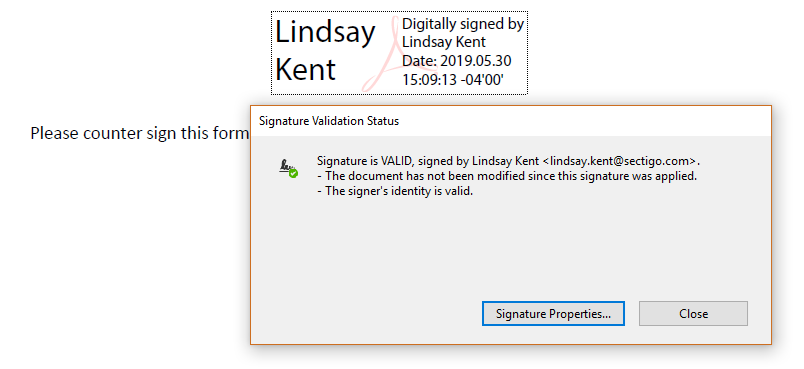
In today’s digital world, it would be completely inefficient to physically sign every document that requires you to do so. That is what brings us to document signing. PKI enables users to electronically sign documents with the ability to prove to the receiver that the signed document is coming from a legitimate source. This happens with document signing certificates. And PKI isn’t just offering a secure way to digitally sign documents, it’s also saving you from a lot of hand cramps.


Comments
Post a Comment