LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a software protocol for enabling anyone to locate data about organizations, individuals and other resources such as files and devices in a network -- whether on the public Internet or on a corporate Intranet. LDAP is a "lightweight" (smaller amount of code) version of Directory Access Protocol (DAP), which is part of X.500, a standard for directory services in a network.
A directory tells the user where in the network something is located. On TCP/IP networks (including the internet), the domain name system (DNS) is the directory system used to relate the domain name to a specific network address (a unique location on the network). However, the user may not know the domain name. LDAP allows a user to search for an individual without knowing where they're located (although additional information will help with the search).
Uses of LDAP
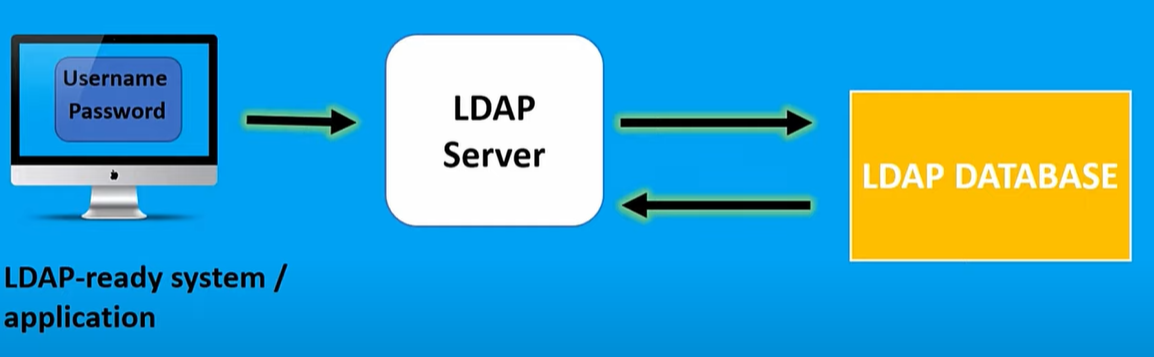
The common use of LDAP is to provide a central place for authentication -- meaning it stores usernames and passwords. LDAP can then be used in different applications or services to validate users with a plugin. As some examples, LDAP can be used to validate usernames and passwords with Docker, Jenkins, Kubernetes, Open VPN and Linux Samba servers. LDAP single sign-on can also be used by system administrators to control access to an LDAP database.
LDAP can also be used to add operations into a directory server database, authenticate -- or bind -- sessions, delete LDAP entries, search and compare entries using different commands, modify existing entries, extend entries, abandon requests or unbind operations.
LDAP is used in Microsoft's Active Directory, but can also be used in other tools such as Open LDAP, Red Hat Directory Servers and IBM Tivoli Directory Servers for example. Open LDAP is an open source LDAP application. It is a Windows LDAP client and admin tool developed for LDAP database control. This tool should allow users to browse, lookup, remove, create and change data that appears on an LDAP server. Open LDAP also allows users to manage passwords and browse by schema.
Red Hat Directory Servers is a tool used to manage multiple systems with a Red Hat Directory Server in a UNIX environment. Red Hat Directory Servers allows users to store user details in an LDAP server. The tool provides users with a secure and restricted access to directory data, group membership and remote access as well as access via validation procedures.
IBM Tivoli Directory Server is an IBM based implementation of LDAP; being based on an LDAP framework. This tool focuses on faster development and distribution of identity control, security and web applications. Tivoli Directory Server includes different validation methods such as validation via digital certificate, Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) and CRAM-MD5.
If an organization is having trouble deciding when to use LDAP, they should consider it in a few use cases. They should consider it if:
- a single piece of data needs to be found and accessed regularly;
- the organization has a lot of smaller data entries;
- the organization wants all smaller pieces of data in one centralized location, and there doesn't need to be an extreme amount of organization between the data.
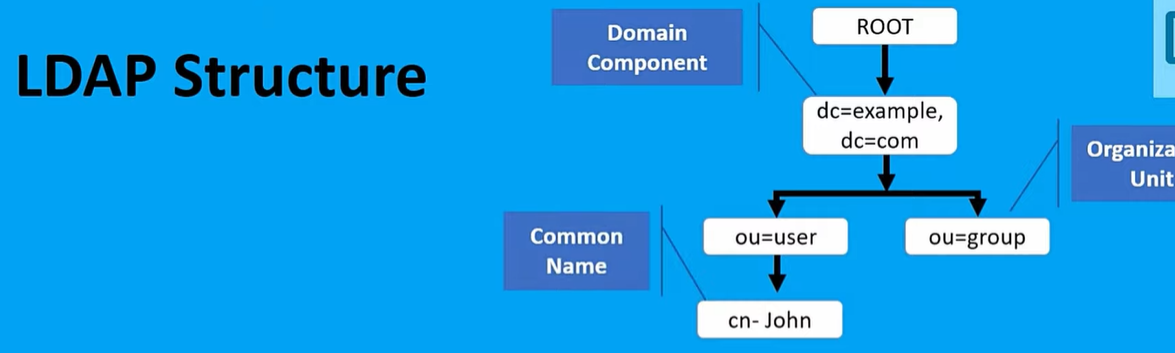
Levels of LDAP directory
An LDAP configuration is organized in a simple "tree" hierarchy consisting of the following levels:
- The root directory (the starting place or the source of the tree), which branches out to:
- Countries, each of which branches out to:
- Organizations, which branch out to:
- Organizational units (divisions, departments and so forth), which branches out to (includes an entry for):
- Individuals (which includes people, files and shared resources such as printers).
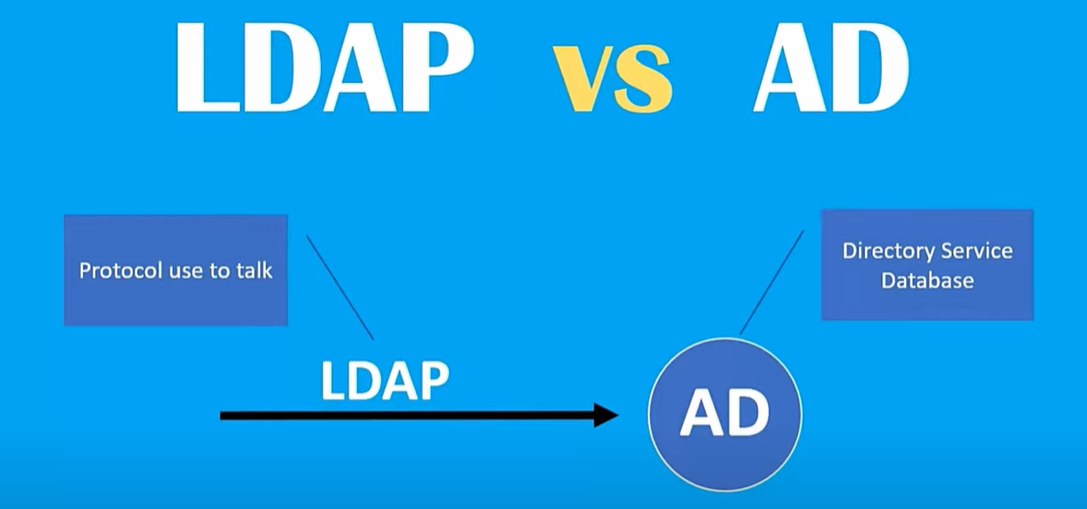
LDAP and Active Directory
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is the protocol that Exchange Server uses to communicate with Active Directory. To really understand what LDAP is and what it does, it is important to understand the basic concept behind Active Directory as it relates to Exchange.
Active Directory is a directory service for managing domains, users and distributed resources such as objects for Windows operating systems. The point behind a directory service is that it manages domains and objects while controlling which users have access to each resource. Active Directory is available on Windows Server 10 and is comprised of multiple services. Services included in Active Directory are Domain, Lightweight Directory, Certificate, Federation and Rights Management services. Each service is included under the Active Directory name to expand directory management capabilities. Active Directory was first previewed in 1999 and has continued to receive updates since then -- including an update with Windows Server 2016 that improved secure Active Directory environments and the ability to migrate Active Directory environments to cloud or hybrid cloud environments.
Active Directory contains information regarding every user account on an entire network. It treats each user account as an object. Each user object also has multiple attributes. An example of an attribute is the user's first name, last name or e-mail address. All this information exists within a huge, cryptic database on a domain controller -- Active Directory. The challenge is to extract information in a usable format. This is LDAP's main job.
LDAP uses a relatively simple, string-based query to extract information from Active Directory. LDAP can store and extract objects such as usernames and passwords in Active Directory, and share that object data throughout a network. The nice part is that this all happens behind the scenes. A regular end user will never have to manually perform an LDAP query, because Outlook is LDAP-enabled and knows how perform all the necessary queries on its own.






Comments
Post a Comment